What to Expect in the Next Generation NCLEX-RN® Test Plan

The NCLEX-RN evaluates your knowledge and abilities for entry-level nursing practice. The exam is built around a 4-category NCLEX-RN test plan — or blueprint. This article provides summaries of each category and subcategory, along with their weight, so you can be as prepared as possible on exam day.
Our guide follows the latest Next Generation NCLEX-RN structure, launched in April 2023. The National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) reviews and updates the exam every 3 years. The next major exam change is expected on March 31, 2026.
NCLEX-RN Test Plan Structure
The NCLEX Examination Committee (NEC) reviews and approves the NCLEX-RN test plan, which includes a content distribution blueprint. Use this blueprint to develop your study plan. The test plan's general structure is:
- Client Needs
- Integrated Processes
- Clinical Judgment
Client Needs
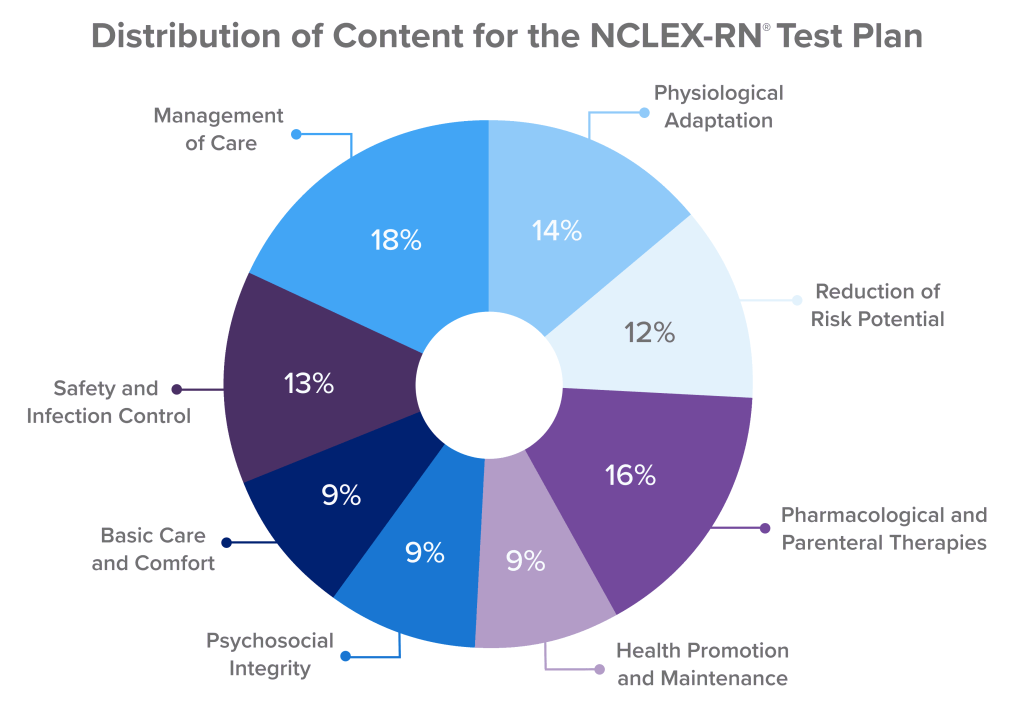
The Client Needs categories are used as a framework for the NCLEX-RN to define the knowledge and skills nurses require to care for clients. Client Needs is divided into 4 main categories, 2 of which are further divided into subcategories.
| Client Needs categories and Subcategories | % of Items |
|---|---|
Safe and Effective Care Environment
|
|
| Health Promotion and Maintenance | 6–12% |
| Psychosocial Integrity | 6–12% |
Physiological Integrity
|
|
Safe and Effective Care Environment
The Safe and Effective Care Environment category carries a 25-37% weighting. It's designed to ensure that RNs can provide safe treatment to patients in a variety of settings and is broken down into the 2 sub-categories:
- Management of Care (15-21%): Nurses with strong management of care skills can prioritize patient needs, delegate tasks to other healthcare professionals, and collaborate with interdisciplinary teams to develop and implement care plans. This category also covers the management of healthcare resources, including time, personnel, and supplies, to ensure that patient care is delivered efficiently and effectively.
- Safety and Infection Control (10-16%): Refers to the steps taken by medical personnel to stop the transmission of infections to patients, employees, and visitors. These precautions include spotting possible risks, putting infection control policies and procedures in place, utilizing personal protective equipment (PPE), keeping oneself clean, and handling and disposing of hazardous materials with care.
Health Promotion and Maintenance
The Health Promotion and Maintenance category carries a 6-12% weighting. This category focuses on activities and interventions that assist people, families, and communities in preserving and enhancing their general health and well-being. This entails:
- Promoting healthy lifestyles
- Preventing illness and injury
- Managing chronic health conditions
- Educating patients about healthy behaviors
- Promoting regular health screenings and vaccinations
- Identifying and addressing health concerns early
The key objectives for healthcare practitioners are maintaining optimal health, preventing or managing chronic diseases, and enhancing patients' overall quality of life. In practice, this can mean assisting patients and their families with the management of chronic illnesses such as diabetes or heart disease, instructing patients on good nutrition, and encouraging patients to quit smoking.
Psychosocial Integrity
The Psychosocial Integrity category carries a 6-12% weighting. You are assessed on your knowledge and abilities in relation to treating patients with mental health and psychosocial problems. Healthcare providers must offer patients holistic care that takes their physical and emotional health into account. Important subjects are:
- Therapeutic communication
- Coping mechanisms
- Mental health disorders
- Substance abuse
- Grief and loss
- Family dynamics
This category provides a framework for understanding the social and emotional aspects that affect a patient's health and well-being. Healthcare workers must be able to provide compassionate care, recognize and address patients' emotional needs, and interact with patients and their families in a clear and effective manner. Examples include recognizing the warning signs of suicide or self-harm, taking into account the adverse effects of psychotropic medications, and putting the proper safety measures in place.
Physiological Integrity
The Physiological Integrity category is divided into 4 subcategories and weighted at 39-63%. You are required to show proficiency in providing safe and effective care to patients with physiological needs. This category focuses on understanding how the human body functions and the disruptive qualities of disease and injury.
Focuses on the fundamentals of nursing care, such as aiding with mobility, controlling discomfort, offering emotional support, and engaging in efficient communication.
Elaborates on how to administer medication in a safe and efficient manner. Includes pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacology principles. You must show that they can keep an eye out for negative drug reactions and put the right measures in place.
Covers the prevention of complications and adverse events such as falls, infections, and complications from surgeries or treatments, as well as how to keep an eye out for drug-related complications and put the right safety precautions in place.
Consists of treating patients who have either acute or long-term physiological abnormalities, such as changes to their vital signs, oxygenation, or fluid/electrolyte balance. This subcategory also covers the skills needed for competent care for patients with acute or chronic illnesses, such as respiratory distress, heart failure, and diabetes.
This category is used in practice in various ways, including bathing, feeding, and positioning a patient with physiological demands. Other uses include administering nutritional and oral hydration, parenteral and pharmaceutical therapy, and emergency care.
Integrated Processes
Nurses must understand how to prioritize patient care, recognize and address patient situation changes, and work well with the rest of the healthcare team. For instance, nurses might need to use information technology to assist with patient care and documentation or apply ethical and legal ideas in various situations. Integrated Processes evaluate your capacity to practice clinical reasoning and critical thinking in all facets of nursing care.
Fostering mutual respect and trust, as well as fostering a compassionate and cooperative environment.
Thinking critically, providing evidence-based solutions, and prioritizing concerns.
Collecting data, planning, implementing, and evaluating to approach client care scientifically.
Includes verbal and nonverbal (i.e., written/electronic records) interactions between nurses, clients, and other healthcare professionals.
Considers a patient’s reported or self-identified preferences and recognizes related legal considerations.
Nurturing a positive learning environment and establishing positive behavior changes.
Clinical Judgment
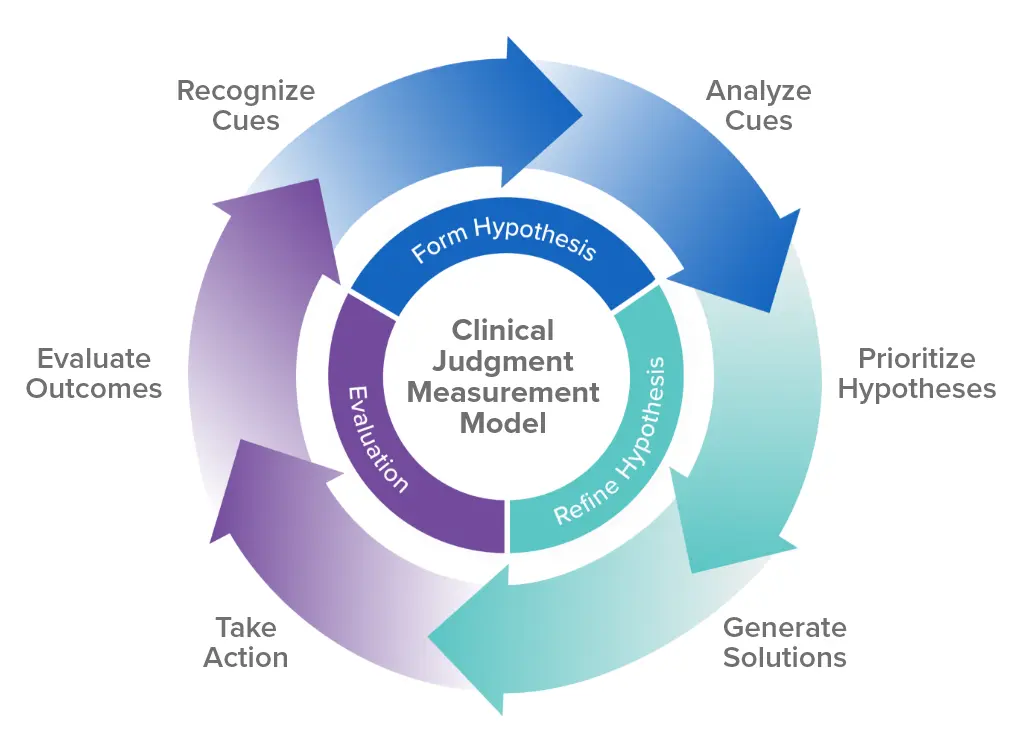
Clinical judgment refers to a nurse's ability to use knowledge, experience, and critical thinking skills to make informed decisions about a patient's care. It involves synthesizing information from various sources, such as patient history, assessments, medical records, and lab data, to develop a treatment plan and evaluate its outcomes.
To ensure all entry-level nurses have the clinical judgment skills necessary to provide safe and effective care, the NCSBN developed the Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM) to provide a framework to better understand and assess clinical judgment. Tier 3 of the NCJMM is focused on 6 measurable steps in the clinical decision-making process.
Administration of the NCLEX-RN
The final section of the NCLEX-RN test plan covers details regarding the administration of the exam — exam length, passing standard, scoring methods, and terminology. Learn more about these details.
This guide provides key information on the NCLEX-RN and NCLEX-PN exams. It covers eligibility requirements, testing procedures, question formats, and scoring methods, including updates on the Next Generation NCLEX (NGN).
NCLEX Eligibility, Registration & Cost
This page offers registration information for the NCLEX-RN and NCLEX-PN exams. It includes details on eligibility requirements, scheduling, and exam costs.
This guide provides a breakdown of NCLEX scoring, pass/fail criteria, and pass rates. It also covers the adaptive testing method, new scoring models introduced with the Next Generation NCLEX, and what constitutes a passing score.
This study guide outlines key NCLEX content areas, introduces question types, and provides practical study tips for aspiring nurses. With sample schedules and study plan examples, it builds a tailored plan for exam day readiness.