2024 Next Generation NCLEX-PN® Test Plan Highlights

Passing the NCLEX-PN is required to become a licensed practical or vocational nurse in the United States. Developed by the National Council of State Board of Nursing® (NCSBN®), the exam is designed to assess a candidate's knowledge and skills as they relate to entry-level nursing practice. The exam is based on an NCLEX-PN test plan, or blueprint, that includes four categories. If you're considering taking this exam, it’s essential that you familiarize yourself with the content of the test plan and use it as a blueprint for your study strategy. This article details each category and subcategory in easily digestible summaries to help you get started.
NCLEX-PN Test Plan Structure
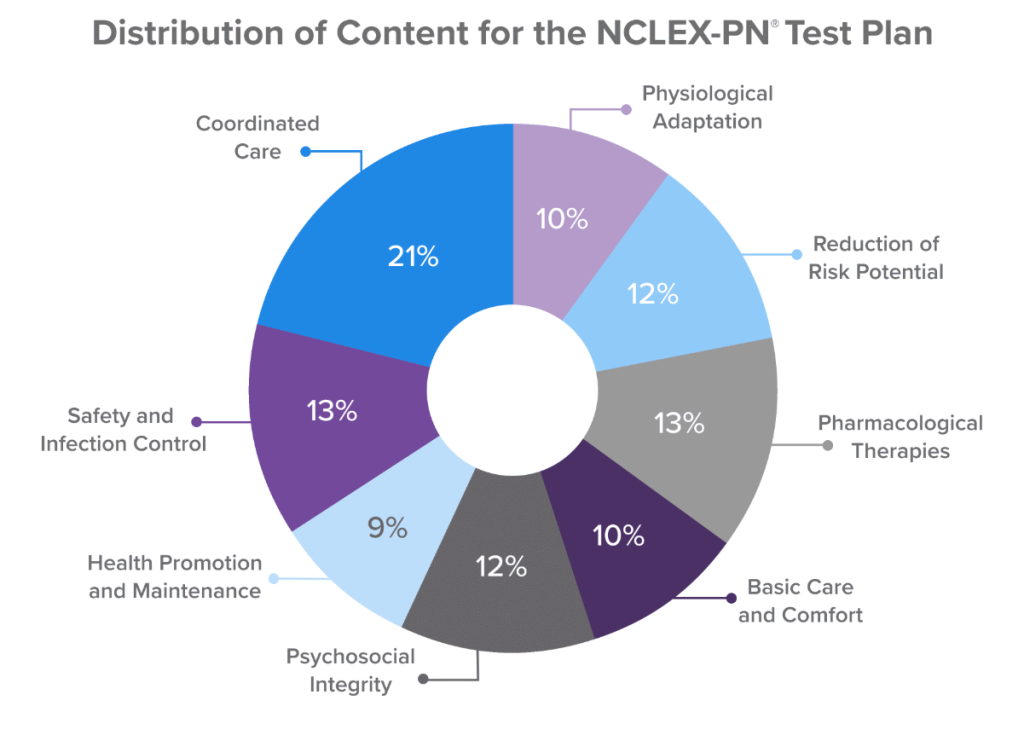
The NCLEX Examination Committee (NEC) is responsible for reviewing and approving the NCLEX-PN test plan. This blueprint contains the exam’s content distribution, which will be critical as you plan your studies. For example, you’re much more likely to come across a question on Coordinated Care than one on Health Promotion and Maintenance. The percentage weight of each client needs category is detailed below. Here’ is the test plan’s general structure:
- Client Needs
- Integrated Processes
- Clinical Judgment
Client Needs Categories
The Client Needs categories provide a framework for defining what skills and knowledge nurses need in order to serve a diverse range of clients from various locales. The NCLEX-PN test plan divides Client Needs into four overarching categories, two of which are further divided into subcategories:
| Client Needs | % of Items |
|---|---|
Safe and Effective Care Environment
|
|
| Health Promotion and Maintenance | 6–12% |
| Psychosocial Integrity | 9-15% |
Physiological Integrity
|
|
Safe and Effective Care Environment
The Safe and Effective Care Environment category is weighted at 28-40% of the NCLEX-PN. Its purpose is to ensure that PNs are capable of delivering safe care to patients in a variety of settings and is divided into the two following sub-categories:
- Coordinated Care (18-24%) — Includes working with other healthcare professionals to ensure patients receive seamless, continuous, and comprehensive care. Tasks include conducting patient assessments, managing medications, and ensuring smooth transitions between different levels of care.
- Safety and Infection Control (10-16%)— Refers to measures taken by healthcare professionals to prevent the spread of infection between patients, staff, and visitors. Such measures include identifying potential hazards, implementing policies and procedures to prevent infection, using personal protective equipment (PPE), practicing good hygiene, and handling/disposing of hazardous material with care.
Health Promotion and Maintenance
The Health Promotion and Maintenance category is weighted at 6-12% of the NCLEX-PN. This category involves activities and interventions that help individuals, families, and communities maintain and improve their overall health and well-being. This involves:
- Promoting healthy lifestyles
- Preventing illness and injury
- Managing chronic health conditions
- Educating patients about healthy behaviors
- Promoting regular health screenings and vaccinations
- Identifying and addressing health concerns early
In action, this may include providing support and guidance to patients and their families as they manage a chronic condition like diabetes or heart disease or educating patients on proper nutrition or smoking cessation. The primary goal here is for healthcare professionals to help their patients prevent or manage chronic diseases, maintain optimal health, and improve their overall quality of life.
Psychosocial Integrity
The Psychosocial Integrity category is weighted at 9-15% of the NCLEX-PN. Examinees will be tested on their knowledge and skills as they relate to providing care to patients with mental health and psychosocial issues. Healthcare professionals must provide holistic care that addresses both the physical and emotional needs of patients. Important topics include:
- Therapeutic communication
- Coping mechanisms
- Mental health disorders
- Substance abuse
- Grief and loss
- Family dynamics
Psychosocial integrity provides a framework for nurses to understand the social and emotional factors that impact a patient's health and well-being. Healthcare professionals must be able to practice compassionate care, assess and respond to patients' emotional needs, and communicate effectively with patients and their families. In action, this may include identifying warning signs of suicide or self-harm or considering the side effects of psychotropic medications and implementing the appropriate safety measures.
Physiological Integrity
The Physiological Integrity category is weighted at 33-57% of the NCLEX-PN and is divided into four sub-categories (see details below). Examinees must demonstrate competency as it relates to providing safe and effective care to patients with physiological needs. This requires understanding the normal functioning of the human body and how it can be affected by illness or injury.
Real-world implementation of this category ranges from monitoring vital signs to bathing, feeding, and positioning a patient with physiological needs. Other applications include providing pharmacological and parenteral therapy, nutrition and oral hydration, and emergency care.
Integrated Processes
Nurses must maintain the ability to prioritize care, identify and respond to changes in the patient’s conditions, and collaborate effectively with the healthcare team. For example, nurses may need to incorporate ethical and legal principles into their practice or use information technology to support patient care and documentation. This requires knowledge and skills from all four client needs categories. With this in mind, Integrated Processes assesses an examinee's ability to apply critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills across all areas of nursing care. The following processes are fundamental to this category:
Clinical Judgment
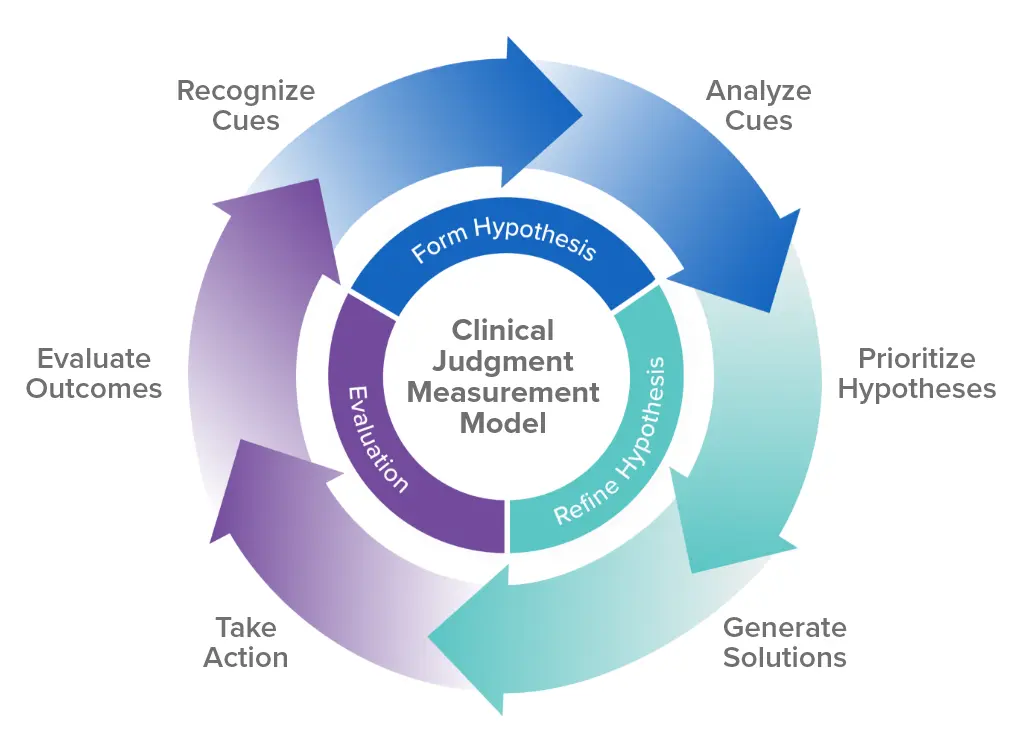
The ability of a nurse to apply their knowledge, experience, and critical thinking abilities to make well-informed decisions concerning a patient's care is referred to as clinical judgment. It entails compiling data from numerous sources, including patient histories, assessments, medical records, and lab results, then applying that knowledge to create treatment plans and analyze their effectiveness.
The NCSBN created the Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM) to provide a framework for better understanding and evaluating candidates' clinical judgment. This was done to emphasize the significance of clinical judgment and ensure that all entry-level nurses have the clinical judgment skills necessary to provide safe and effective care. Six quantifiable processes in the clinical decision-making process are the emphasis of the NCJMM's third tier.
Administration of the NCLEX-PN
Every three years, the NEC updates the NCLEX-PN test plan so that it continues to be an accurate reflection of an examinees ability to practice entry-level nursing. The last section of the test plan details the exam’s administration. This includes detailed information on the passing standard, exam length, scoring methods, and terminology. See the articles below for more information on the administration of the NCLEX-PN.
There is so much to know about the NCLEX. That's why we've filtered the most important information from across the internet on this page.
NCLEX Eligibility, Registration & Cost
You can't pass an exam that you can't take. Learn whether or not you're eligible, how to register, and how much you'll need to pay to take the NCLEX.
Computerized adaptive testing (CAT) can be a bit intimidating. Check out this guide where we simplify the NCLEX scoring process.
Now that you know what the NCLEX-PN covers, it’s time to develop a comprehensive and effective plan. Our study guide will help you get started.