Free Dosage Calculation
Sample Questions
Practicing with dosage calculation sample questions and learning from your mistakes is the secret to passing your next Med Math test!
Dosage Calculations For Every Level of Nursing School
Our dosage calculations questions are organized by difficulty level and cover the full range of medication categories so you are ready to pass any med math test and become a safe practicing nurse.
Benefit from
Exam-Like Practice
Learn From
Detailed Rationales
Customize Tests
to Your Needs
Dosage Calculation Sample Questions
Our detailed answer explanations walk you step-by-step through dosage calculation problems using both dimensional analysis and an alternate calculation method. Try some out for yourself:
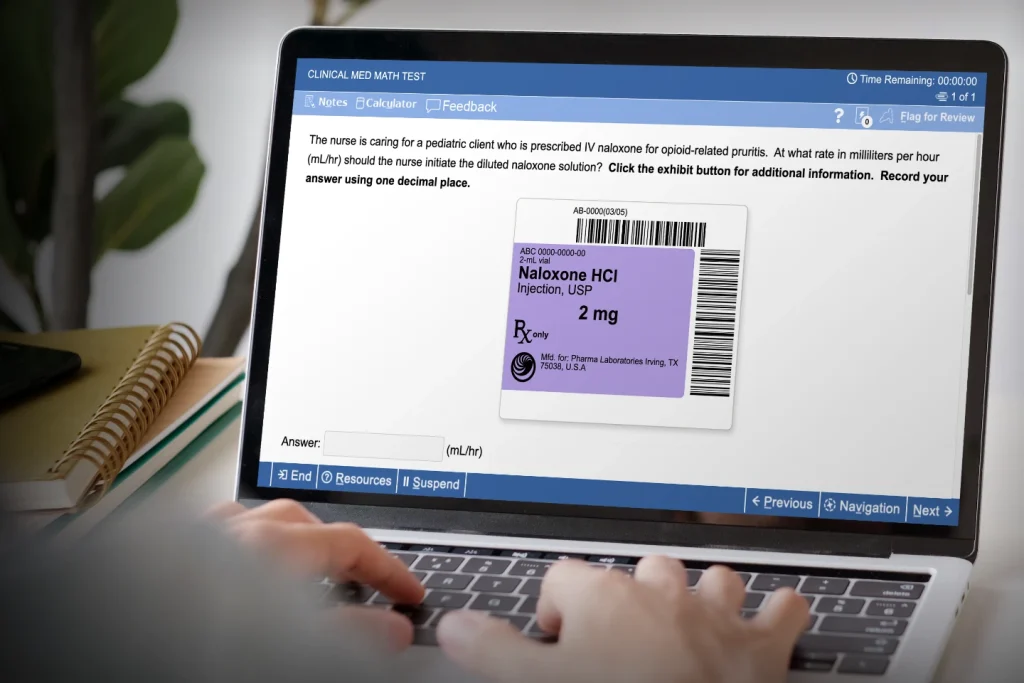
The nurse is caring for a pediatric client who is prescribed IV naloxone for opioid-related pruritis. At what rate in milliliters per hour (mL/hr) should the nurse initiate the diluted naloxone solution? Click the exhibit button for additional information. Record your answer using one decimal place.
| Answer: (mL/hr) |
Correct Answer : 13.2 mL/hr
Explanation:
Using dimensional analysis, perform the following steps to calculate the infusion rate in milliliters per hour of naloxone (NAL) diluted in normal saline (NS):
-
Identify the prescribed, available, and required medication information
Prescribed: 2 mcg NAL / kg | hr Available: 2 mg NAL / 2 mL Required: mL NAL / hr
-
Identify the final diluted medication volume
Dilution instructions: infusion bag - medication volume + medication
OR
500 mL NS - 2 mL NS + 2 mL NAL = 500 mL diluted NAL or 2 mg NAL / 500 mL
-
Convert the prescription to the infusion rate of NAL in milliliters per hour
Prescription x diluted medication = mL NAL / hr
OR
( mcg NAL / kg | hr ) ( kg / lb ) ( lb / )( mg / mcg ) ( mL / mg NAL ) = mL NAL / hr
OR
( 2 mcg NAL / kg / hr ) ( kg / 2.2 lb ) ( 58 lb / )( mg / 1000 mcg ) ( 500 mL / 2 mg NAL ) = 13.1818 mL NAL / hr
-
Round to one decimal place
13.1818 mL NAL / hr ≈ 13.2 mL NAL / hr
Educational objective:
To calculate the infusion rate of naloxone diluted in normal saline, the nurse should first identify the prescribed dose (eg, 2 mcg/kg/hr), available medication (eg, 2 mg/2 mL), and diluted volume (eg, 2 mg/500 mL) and then convert to milliliters per hour (eg, 13.2 mL/hr).
Alternative Method:
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round any calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, perform the following steps to calculate the infusion rate in milliliters per hour of naloxone (NAL) diluted in normal saline (NS):
-
Convert the weight to kilograms
( kg / 2.2 lb ) ( 58 lb / ) = 26.3636 kg
-
Calculate the dose in micrograms per hour
( 2 mcg NAL / kg | hr ) ( 26.3636 kg / ) = 52.7272 mcg NAL / hr
-
Convert the prescription to milligrams per hour
( 52.7272 mcg NAL / hr ) ( mg / 1000 mcg ) = 0.0527 mg NAL / hr
-
Identify the final diluted medication volume
Dilution instructions: infusion bag - medication volume + medication
OR
500 mL NS - 2 mL NS + 2 mL NAL = 500 mL diluted NAL or 2 mg NAL / 500 mL
-
Convert the prescription to the infusion rate of NAL in milliliters per hour
Prescribed dose / diluted dose x diluted volume = mL NAL / hr
OR
0.0527 mg NAL / 2 mg NAL x 500 mL = 13.1818 mL NAL / hr
-
Round to one decimal place
13.1818 mL NAL / hr ≈ 13.2 mL NAL / hr
The nurse is preparing IV pancuronium for a client who is about to undergo endotracheal intubation. How many milliliters per dose (mL/dose) should the nurse administer? Click the exhibit button for additional information. Record your answer using one decimal place.
| Answer: (mL/dose) |
Correct Answer : 6.3 mL/dose
Explanation:
Using dimensional analysis, perform the following steps to calculate the administration volume of pancuronium (PAN) in milliliters per dose:
-
Identify the prescribed, available, and required medication information
Prescribed: 0.06 mg PAN / kg | dose Available: 1 mg PAN / mL Required: mL PAN / dose
-
Convert the prescription to the infusion rate of PAN in milliliters per hour
Prescription x available medication = mL PAN / dose
OR
( mg PAN / kg | dose ) ( kg / lb ) ( lb / )( mL / mg PAN ) = mL PAN / dose
OR
( 0.06 mg PAN / kg | dose ) ( kg / 2.2 lb ) ( 231 lb / )( mL / 1 mg PAN ) = 6.3 mL PAN / dose
Educational objective:
To calculate the administration volume of pancuronium, the nurse should first identify the prescribed dose (eg, 0.06 mg/kg/dose) and available medication (eg, 1 mg/mL) and then convert to milliliters per dose (eg, 6.3 mL/dose).
Alternative Method:
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round any calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, perform the following steps to calculate the administration volume of pancuronium (PAN) in milliliters per dose:
-
Convert the weight to kilograms
( kg / 2.2 lb ) ( 231 lb / ) = 105 kg
-
Calculate the prescribed dose in milligrams per dose
( 0.06 mg PAN / kg | dose ) ( 105 kg / ) = 6.3 mg PAN / dose
-
Convert the prescription to the administration volume of PAN in milliliters per dose
Prescribed dose / available dose x available volume = mL PAN / dose
OR
6.3 mg PAN / 1 mg PAN x mL = 6.3 mL PAN / dose
The nurse is caring for a client with osteoporosis who is receiving PO alendronate. How many milliliters per dose (mL/dose) of alendronate should the nurse administer? Click the exhibit button for additional information. Record your answer using one decimal place.
| Answer: (mL/dose) |
Correct Answer : 5.4 mL/dose
Explanation:
Using dimensional analysis, perform the following steps to calculate the administration volume of alendronate (ALN) in milliliters per dose:
-
Identify the prescribed, available, and required medication information
Prescribed: 5 mg ALN / dose Available: 70 mg ALN / 75 mL Required: mL ALN / dose
-
Convert the prescription to the administration volume of ALN in milliliters per dose
Prescription x available medication = mL ALN / dose
OR
( mg ALN / dose ) ( mL / mg ALN ) = mL ALN / dose
OR
( 5 mg ALN / dose ) ( 75 mL / 70 mg ALN ) = 5.3571 ... mL ALN / dose
-
Round to one decimal place
5.3571 ... mL ALN / dose ≈ 5.4 mL ALN / dose
Educational objective:
To calculate the administration volume of alendronate, the nurse should first identify the prescribed dose (eg, 5 mg/dose) and available medication (eg, 70 mg/75 mL) and then convert to milliliters per dose (eg, 5.4 mL/dose).
Alternative Method:
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round any calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, perform the following steps to calculate the administration volume of alendronate (ALN) in milliliters per dose:
-
Convert the prescription to the administration volume of ALN in milliliters per dose
Prescribed dose / available dose x available volume = mL ALN / dose
OR
5 mg ALN / 70 mg ALN x 75 mL = 5.3571 ... mL ALN / dose
-
Round to one decimal place
5.3571 ... mL ALN / dose ≈ 5.4 mL ALN / dose
The nurse is administering 2.8 mL of hydromorphone to a pediatric client who weighs 61 lb and reports pain. How many milligrams per kilogram per dose (mg/kg/dose) is the nurse administering? Record your answer using one decimal place.
| Answer: (mg/kg/dose) |
Correct Answer : 0.1 mg/kg/dose
Explanation:
Using dimensional analysis, perform the following steps to calculate the prepared dose of hydromorphone (HM) in milligrams per kilogram:
-
Identify the prepared volume, available medication, client's weight, and required units
Volume: 2.8 mL HM / dose Available: 1 mg HM / mL Weight: 61 lb / Required: mg HM / kg | dose
-
Convert the administration volume to the prepared dose of HM in milligrams per kilogram
Volume x available medication ÷ weight = mg HM / kg | dose
OR
( mL HM / dose ) ( mg HM / mL ) ( lb / kg ) ( / lb ) = mg HM / kg | dose
OR
( 2.8 mL HM / dose ) ( 1 mg HM / mL ) ( 2.2 lb / kg ) ( / 61 lb ) = 0.1009 ... mg HM / kg | dose
-
Round to one decimal place
0.1009 ... mg HM / kg | dose ≈ 0.1 mg HM / kg | dose
Educational objective:
To calculate the prepared dose of hydromorphone, the nurse should first identify the administration volume (eg, 2.8 mL/dose),available medication (eg, 1 mg/mL), and client's weight (61 lb) and then convert to the dose (eg, 0.1 mg/kg/dose).
Alternative Method:
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round any calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, perform the following steps to calculate the prepared dose of hydromorphone (HM) in milligrams per kilogram:
-
Convert the weight to kilograms
( kg / 2.2 lb ) ( 61 lb / ) = 27.7272 kg
-
Convert the administration volume of HM to the prepared dose in milligrams
Administration volume / available volume x available dose = mg HM / dose
OR
2.8 mL HM / mL HM x 1 mg = 2.8 mg HM / dose
-
Convert the prepared dose to the weight-based dose of HM
( 2.8 mg HM / dose ) ( / 27.7272 kg ) = 0.1009 ... mg HM / kg | dose
-
Round to one decimal place
0.1009 ... mg HM / kg | dose ≈ 0.1 mg HM / kg | dose
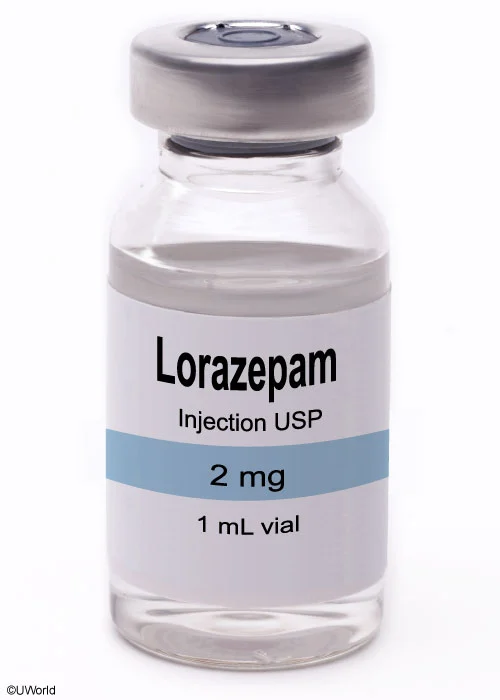
The nurse is caring for a client having a tonic-clonic seizure who is prescribed 4 mg lorazepam IV push STAT. What is the total volume of reconstituted lorazepam in milliliters per dose (mL/dose) to be administered? Click the exhibit button for additional information. Record your answer using one decimal place.
| Answer: (mL/dose) |
Correct Answer : 4 mL/dose
Explanation:
Using dimensional analysis, perform the following steps to calculate the total diluted volume in milliliters per dose of lorazepam:
-
Identify the prescribed, available, and required medication information
Prescribed: 4 mg lorazepam / dose Available: 2 mg lorazepam / mL Required: mL lorazepam / dose
-
Convert the prescription to the volume of lorazepam in milliliters per dose
Prescription x available medication = mL lorazepam / dose
OR
( mg lorazepam / dose ) ( mL / mg lorazepam ) = mL lorazepam / dose
OR
( 4 mg lorazepam / dose ) ( mL / 2 mg lorazepam ) = 2 mL lorazepam / dose
-
Add the dilution volume to the medication for total administration volume
Concentration: 1 mL diluent per 1 mL lorazepam
OR
2 mL lorazepam + 2 mL diluent = 4 mL total solution
Educational objective:
To calculate the total administration volume in milliliters of lorazepam, the nurse should first identify the prescribed dose (eg, 4 mg), available medication (eg, 2 mg/mL), and diluent needed (eg, 1 mL diluent per 1 mL lorazepam) and then calculate the total milliliters per dose (eg, 4 mL/dose).
Alternate Method:
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round any calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, perform the following steps to calculate the total diluted volume in milliliters per dose of lorazepam:
-
Convert the prescription to the volume of lorazepam in milliliters per dose
Prescribed dose / required concentration x volume = mL lorazepam / dose
OR
4 mg lorazepam / 2 mg lorazepam x mL = 2 mL lorazepam / dose
-
Add the dilution volume to the medication
Concentration: 1 mL diluent per 1 mL lorazepam
OR
2 mL lorazepam + 2 mL diluent = 4 mL total solution
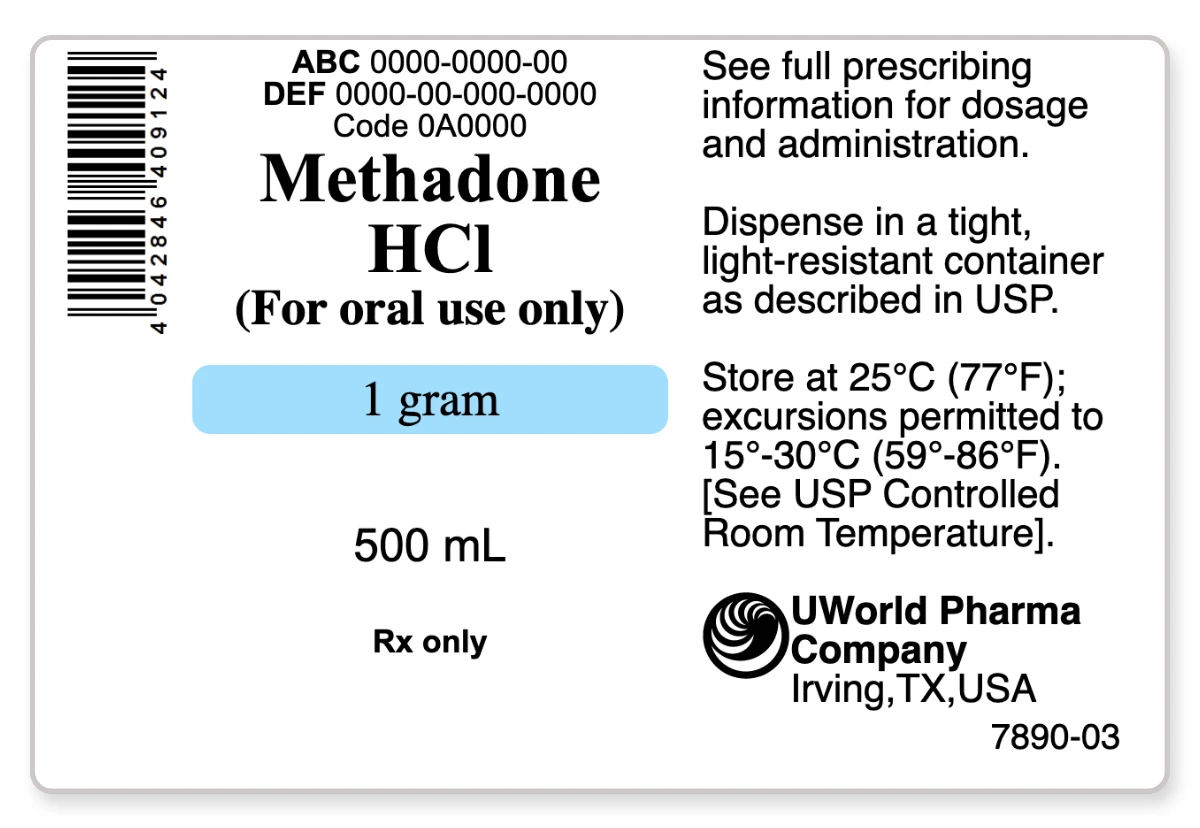
The nurse is caring for a client with severe pain who is prescribed PO methadone. How many milliliters per dose (mL/dose) of methadone should the nurse administer? Click the exhibit button for additional information. Record your answer using one decimal place.
| Answer: (mL/dose) |
Correct Answer : 2.5 mL/dose
Explanation:
Using dimensional analysis, perform the following steps to calculate the administration volume of methadone in milliliters per dose:
-
Identify the prescribed, available, and required medication information
Prescribed: 0.1 mg methadone / kg | dose Available: 1 g methadone / 500 mL Required: mL methadone / dose
-
Convert the prescription of methadone to the volume in milliliters per dose
Prescription x available concentration = mL methadone / dose
OR
( mg methadone / kg | dose ) ( kg / lb ) ( lb / ) ( g / mg )( mL / g methadone ) = mL methadone / dose
OR
( 0.1 mg methadone / kg | dose ) ( kg / 2.2 lb ) ( 108 lb / ) ( g / 1000 mg )( 500 mL / 1 g methadone ) = 2.4545 mL methadone / dose
-
Round to one decimal place
2.4545 mL methadone / dose ≈ 2.5 mL methadone / dose
Educational objective:
To calculate the administration volume of methadone, the nurse should first identify the prescribed dose (eg, 0.1 mg/kg/dose) and available concentration (eg, 1 g/500 mL) and then convert to milliliters per dose (eg, 2.5 mL/dose).
Alternative Method:
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round any calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, perform the following steps to calculate the administration volume of methadone in milliliters per dose:
-
Convert the weight to kilograms
( 108 lb / ) ( kg / 2.2 lb ) = 49.0990 kg
-
Calculate the prescribed dose in milligrams
( 0.1 mg methadone / kg | dose ) ( 49.0990 kg / ) = 4.9090 mg methadone / dose
-
Convert the dose to grams
( 4.9090 mg methadone / dose ) ( g / 1000 mg ) = 0.0049 ... g methadone / dose
-
Convert the prescription of methadone to the volume in milliliters per dose
Prescribed dose / available medication x available volume = mL methadone / dose
OR
0.0049 ... g methadone / 1 g methadone x 500 mL = 2.4545 mL methadone / dose
-
Round to one decimal place
2.4545 mL methadone / dose ≈ 2.5 mL methadone / dose
Pass Your Next Dosage Calculation Test
The Clinical Med Math QBank includes up to four 29-question self-assessment tests in addition to 75+ sequenced case scenarios to build your clinical judgment skills.
UWorld Nursing Student Testimonials
We measure the success of our test prep products by the success of our users. Here’s what UWorld Nursing students are saying:
UWorld brings challenging dosage calc questions and up-to-date rationales. I love it.”
Thank you for having such an amazing variety of questions, and the rationales are AMAZING.”
I love that I get to pick and choose directly what to study so I'm not wasting my time on things I already know.”