A client with type I diabetes mellitus comes to the emergency department with deep respirations of 36/min, abdominal pain, and fruity breath; the client also appears lethargic. The nurse should anticipate which of the following prescriptions? Select all that apply.
Below is the code for an example image modal link
Flashcards
/* -- Un-comment the code below to show all parts of question -- */
| A. Administer a 1 L 0.9% sodium chloride IV bolus | ||
| B. Initiate an IV infusion of regular insulin | ||
| C. Instruct client to breathe into a paper bag | ||
| D. Obtain blood specimens for a serum glucose test | ||
| E. Place the client on continuous cardiac monitoring |
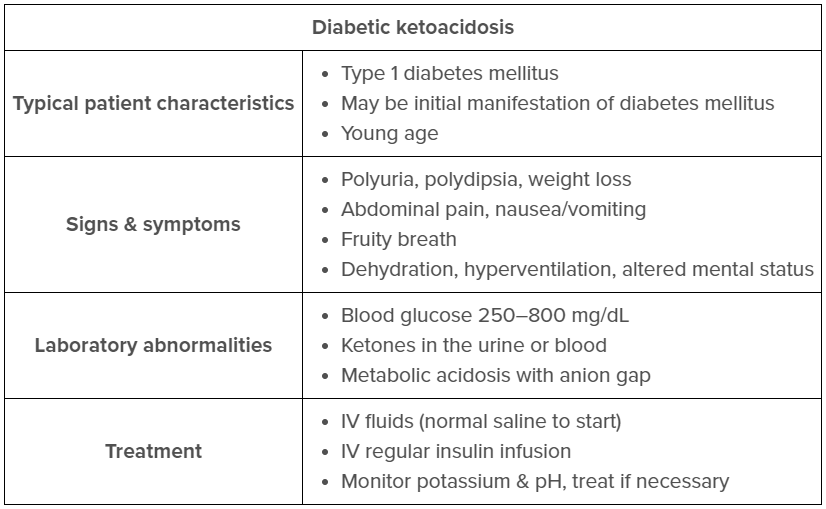
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus that results from a lack of insulin. Insulin is required to transport glucose into cells for energy; therefore, lack of insulin leads to intracellular starvation despite a high level of glucose circulating in the blood (ie, hyperglycemia). Physiologic responses to hyperglycemia include polyuria, electrolyte imbalances, and metabolic acidosis that can lead to life-threatening complications (eg, hypovolemic shock, cardiac arrhythmias) without prompt intervention.
The priority intervention for DKA is fluid resuscitation to restore intravascular volume and organ perfusion. The nurse should anticipate a prescription to infuse a bolus of 0.9% sodium chloride, followed by a continuous infusion (Option 1).
Next, the nurse should anticipate:
- Initiating a continuous regular insulin infusion. Blood glucose should be monitored hourly to prevent hypoglycemia (Option 2).
- Obtaining serum blood glucose levels to confirm hyperglycemia (Option 4).
- Initiating continuous cardiac monitoring due to the increased risk for cardiac dysrhythmias secondary to electrolyte imbalances resulting from osmotic diuresis (Option 5).
(Option 3) Kussmaul respirations are deep, rapid breaths that have a fruity smell as CO2 is exhaled. The respirations are a compensatory mechanism to lower PaCO2 and combat metabolic acidosis that should not be inhibited by breathing into a paper bag.
Educational objective:
For the client with diabetic ketoacidosis, the nurse should expect to administer a 1 L 0.9% sodium chloride IV bolus, initiate continuous insulin IV infusion, obtain serum glucose levels, and initiate continuous cardiac monitoring due to the risk for cardiac arrhythmias secondary to electrolyte imbalances.
Lecture References :
- Adult Health - Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)