Gastrointestinal/nutritional
A 25-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of intermittent abdominal pain for the last several years. The pain is crampy without radiation, and the patient rates it as 6 on a scale of 0-10. She also has worsening fatigue and intermittent diarrhea but no blood in the stool. The patient has no nausea, vomiting, or constipation. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F). On examination, the abdomen is tender, without guarding or rebound. There is a draining fistula near the coccyx. Which of the following is likely diagnosis in this patient?
Below is the code for an example image modal link
Flashcards
/* -- Un-comment the code below to show all parts of question -- */
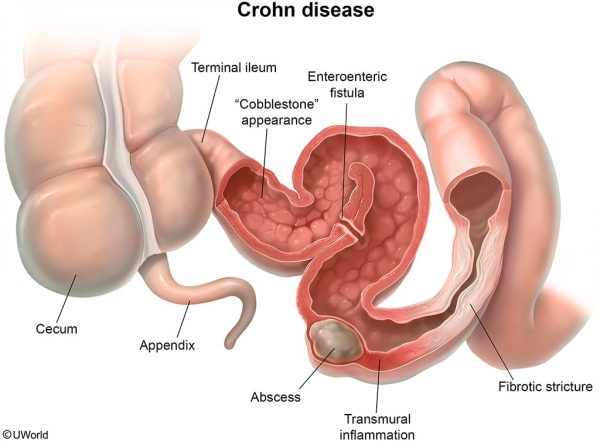
This patient likely has Crohn disease complicated by a perianal fistula. Crohn disease can involve the gastrointestinal tract anywhere from the mouth to the anus, but it often spares the rectum. Patients typically present with bouts of crampy abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constitutional symptoms (eg, fatigue, weight loss, fever) that have occurred over a prolonged period (eg, months or years). Fecal occult blood testing is often positive; however, grossly bloody stool is less common, unless the colon is involved.
Patients are prone to developing fistulae and abscesses due to transmural bowel inflammation. Fistulae usually form between the bowel and nearby structures, including the skin, urinary bladder, or vagina. Perianal disease other than fistulae is also common and may include skin tags and fissures.
(Choice B) Diverticulitis is characterized by inflammation of saclike protrusions (ie, diverticula) that typically form in the sigmoid colon of older patients. It can present with left lower quadrant abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, low-grade fever, and fistulae; however, this patient’s young age makes the diagnosis less likely.
(Choice C) A Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is characterized by chronic abdominal pain associated with altered bowel habits (eg, diarrhea and/or constipation). Pain is often relieved with bowel movements. IBS is not an inflammatory condition and does not cause fistulae.
(Choice D) Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory disease of the colonic mucosa that almost always affects the rectum and often presents with grossly bloody stool. Fistulae are not commonly seen because inflammation does not involve the full thickness of the bowel wall.
Educational objective:
Crohn disease typically presents with the insidious onset of abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constitutional symptoms (eg, fatigue, weight loss, fever). Patients are prone to developing fistulae/abscesses because the lesions affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall. Perianal disease (eg, skin tags, fissures) is also common.
Copyright © UWorld. All rights reserved.