Child Health
Sample Question
The nurse in the emergency department is caring for a pediatric client.
Complete the following sentence by choosing from the list of options.
The nurse should recognize that this condition is most commonly caused by _______
| influenza type A | ||
| Bordetella pertussis | ||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b |
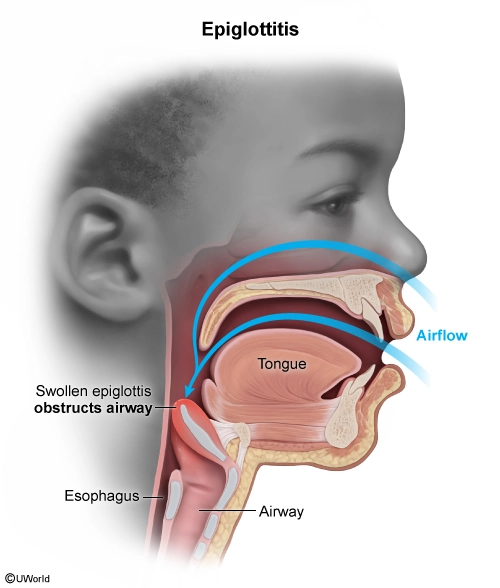
Epiglottitis is inflammation of the tissues surrounding the epiglottis, a long, narrow structure that closes off the glottis during swallowing. Edema can develop rapidly and obstruct the airway by occluding the trachea. Manifestations include sudden-onset high fever, drooling, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), agitation, lack of spontaneous cough, and acute respiratory distress.
In children, epiglottitis is typically caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib). A vaccine protects children from Hib infections (eg, epiglottitis, meningitis, pneumonia) and is part of the recommended immunization schedule for infants and children. Epiglottitis is rarely seen in vaccinated children.
(Incorrect) Influenza type A is a contagious viral infection that affects the respiratory tract. Annual vaccination with either the live attenuated or the inactivated influenza vaccine is recommended to prevent infection.
(Incorrect) Pertussis (ie, whooping cough) is a respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Administration of the diphtheria-tetanus-acellular-pertussis (DTaP) vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the development and spread of pertussis.
Educational objective:
Epiglottitis (inflammation of the epiglottis) is usually caused by a bacterial infection of the upper airway, typically by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib). A vaccine protects children from Hib infections and is part of the recommended schedule of vaccines for infants and children.
- Child Health - Acute Pediatric Epiglottitis





