NCLEX® Practice Questions
Try the Best NCLEX Practice Questions — Free
The best way to become familiar with NCLEX-style questions is through practice. Choose your exam below to experience the UWorld difference.
Question
The nurse is caring for a client at 39 weeks gestation who is receiving an IV oxytocin infusion for induction of labor. The nurse notes recurrent late decelerations on the fetal monitor. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
| 1. Administer an IV fluid bolus. | |
| 2. Reposition the client laterally. | |
| 3. Discontinue the IV oxytocin infusion. | |
| 4. Prepare the client for an amnioinfusion. | |
| 5. Apply abdominal vibroacoustic stimulation. |
Explanation
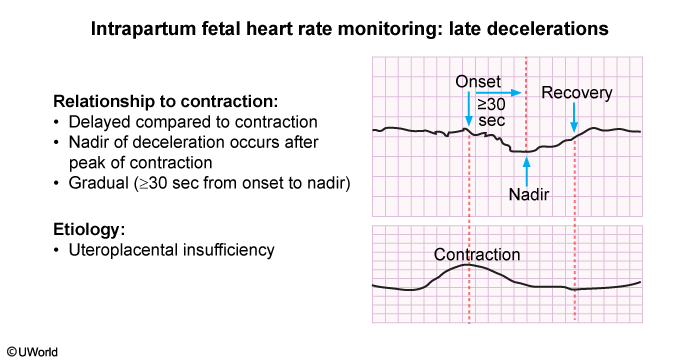
A late deceleration is a decrease in fetal heart rate (FHR) that occurs after the onset of a contraction and continues beyond its end. The lowest point (ie, nadir) occurs near the end of the contraction before the FHR gradually returns to baseline.
Late decelerations occur as a response to temporary fetal hypoxemia. Uteroplacental insufficiency, uterine tachysystole, and maternal supine hypotension are common causes because they compromise perfusion and oxygen availability to the fetus.
Intrauterine resuscitation interventions include:
-
Administering an IV fluid bolus to increase maternal blood volume (Option 1)
-
Repositioning the client laterally to relieve compression of the maternal inferior vena cava, which can be occluded by the weight of the gravid uterus when supine (Option 2)
-
Discontinuing the IV oxytocin infusion to reduce uterine stimulation and decrease contraction frequency; relaxation of the uterus increases uteroplacental blood flow and fetal oxygenation (Option 3)
(Option 4) An amnioinfusion (ie, instillation of fluid into the uterine cavity) is indicated to relieve persistent, recurrent variable decelerations caused by umbilical cord compression.
(Option 5) Vibroacoustic stimulation is used during nonreactive nonstress testing (ie, no accelerations) to provoke fetal movement. It is never performed during FHR decelerations or fetal bradycardia.
Educational objective:
Late decelerations of fetal
heart rate indicate
compromised fetal oxygenation. Intrauterine resuscitation interventions include administering
an IV fluid bolus, discontinuing the IV oxytocin infusion, and repositioning the client laterally.
Question
The nurse is assigning client care activities to a licensed practical nurse (LPN) and unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which of the following activities would be appropriate to assign to the LPN? Select all that apply.
| 1. Administer the daily dose of subcutaneous insulin glargine to a client. | |
| 2. Administer a scheduled oral analgesic to a client who had surgery 2 days ago. | |
| 3. Reinforce teaching about self-administration of insulin for a client with diabetes mellitus. | |
| 4. Complete an admission assessment for a client admitted for an elective hysterectomy. | |
| 5. Record client intake and output totals during the shift for all clients on the unit. |
Explanation
| Scope of practice | ||
|---|---|---|
| RN | LPN/LVN | UAP |
|
|
|
|
*Limited assessments (eg, lung sounds, bowel sounds, neurovascular checks). LPN = licensed practical nurse; LVN = licensed vocational nurse; RN = registered nurse; UAP = unlicensed assistive personnel. |
||
Nurses preparing to delegate client care to a licensed practical nurse (LPN) and/or unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should consider the 5 rights of delegation. The LPN can monitor and care for stable clients who have been initially evaluated by a registered nurse (RN). Interventions that LPNs may perform include:
- Administering most medications (eg, subcutaneous insulin, oral analgesics) (Options 1 and 2)
- Reinforcing teaching and skills that have been initially taught by the RN (Option 3)
- Performing focused assessments (eg, bowel sounds) after the RN's initial assessment
(Option 4) Performing admission or initial assessments is outside the scope of the LPN and UAP. The RN must perform initial assessments to analyze the findings and formulate the client's plan of care before delegating tasks.
(Option 5) The LPN is capable of performing routine care (eg, calculating daily intake and output, toileting). However, the UAP may also perform these tasks, which frees the LPN to perform more complex duties. Therefore, the most appropriate staff member to assign the task of calculating intake and output is the UAP.
Educational objective:
Nurses preparing to delegate
client care should consider the 5 rights of delegation. Appropriate tasks to delegate to a
licensed practical nurse include the administration of oral and parenteral medications (excluding
those via the IV route) and reinforcement of teaching previously provided by the registered nurse.
Question
The nurse is caring for a client with panic disorder who is reporting palpitations and intense feelings of fear. The client is shaking and hyperventilating. Which of the following actions would be a priority for the nurse to take?
| 1. Assess the client for auditory and visual hallucinations. | |
| 2. Administer a benzodiazepine to the client. | |
| 3. Explore possible triggers for the episode with the client. | |
| 4. Remain in the room with the client. |
Explanation
Panic disorder involves recurrent, brief (eg, 10- to 30-min) episodes (ie, panic attacks) during which a client experiences sudden, intense fear; anxiety; and physiological discomfort. These attacks often occur unpredictably, without an obvious trigger. Panic disorder may result from an imbalance of neurotransmitters (eg, excess norepinephrine, inadequate serotonin) or an overactivation of the amygdala.
Symptoms of a panic attack resemble many cardiac and respiratory conditions and include a fear of dying, trembling, hyperventilating, palpitations, and shortness of breath. During a panic attack, the nurse should stay with the client to promote safety and offer support (Option 4). In addition, the nurse should remain calm; use simple, clear phrases when providing instruction; and encourage the client to take slow, deep breaths if hyperventilation occurs.
(Option 1) Assessing the client for auditory and visual hallucinations may provide the nurse with information about the severity of the panic attack, but it does not ensure the client's safety.
(Option 2) Benzodiazepines (eg, alprazolam, lorazepam) may help to calm the client, but medication should be considered only if nonpharmacological methods (eg, reducing stimuli) are unsuccessful.
(Option 3) Discussing triggers for the panic attack is not appropriate while the client is symptomatic. Once the client has calmed down, the nurse can discuss possible triggers, evaluate stressors in the client's life, and assist in identifying prevention strategies.
Educational objective:
Panic disorder involves recurrent, brief episodes during
which a client experiences sudden, intense anxiety. During a panic attack, the nurse should
prioritize staying with the client to promote safety and offer support.
- Mental Health - Panic Disorder
Question
The nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for cefuroxime 30 mg/kg/day PO in 2 divided doses. The client weighs 35 lb (15.9 kg). The nurse has cefuroxime 250 mg/5 mL available. How many mL should the nurse administer to the client with each dose? Record your answer using 1 decimal place.
mL/dose
Explanation
Correct Answer: 4.8 mL/dose
Using dimensional analysis, perform the following steps to calculate the volume of cefuroxime in milliliters per dose:
-
Identify the prescribed, available, and required medication information
-
Convert the prescription to the volume needed for administration
OR
OR
-
Round to 1 decimal place
Educational objective:
To calculate the volume of cefuroxime in milliliters per dose, the nurse should first identify the prescribed dose (eg, 30 mg/kg/day) and available medication (eg, 250 mg/5 mL) and then convert to the volume in milliliters per dose (eg, 4.8 mL).
Alternate Method :
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, perform the following steps to calculate the volume of cefuroxime in milliliters per dose:
-
Calculate the prescribed dose in milligrams
-
Convert the prescription to the volume needed for administration
OR
-
Round to 1 decimal place
Question
The nurse is caring for a client with suspected appendicitis who has vomiting and right lower quadrant pain. It would be a priority for the nurse to
| 1. administer oral pain medication | |
| 2. obtain a urine specimen for urinalysis | |
| 3. initiate an IV infusion of 0.9% sodium chloride | |
| 4. obtain a blood specimen for complete blood count and serum electrolyte levels |
Explanation
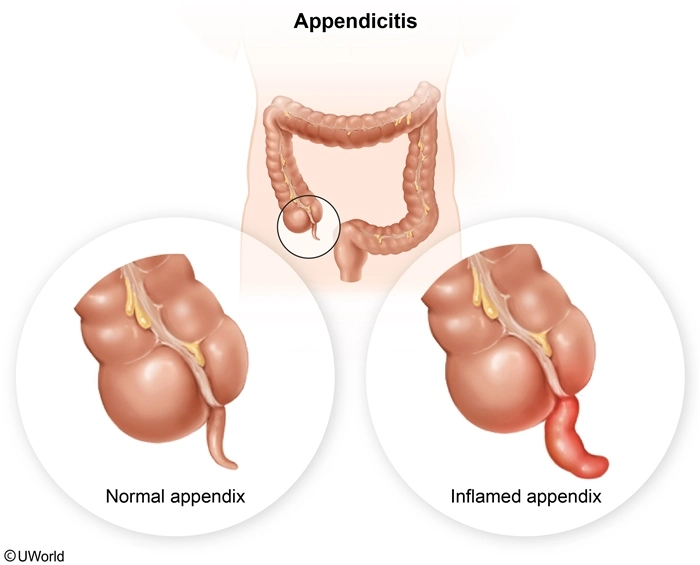
Appendicitis (ie, inflammation of the appendix) often results from obstruction by fecal matter. The obstruction traps fluid and mucus typically secreted into the colon, causing increased intraluminal pressure and inflammation. This impairs blood circulation to the appendix, resulting in swelling and ischemia. These factors increase the risk for perforation, a medical emergency that can lead to peritonitis and sepsis.
When prioritizing care of the client with appendicitis, the nurse should utilize the ABCs (ie, Airway, Breathing, Circulation). Fluid resuscitation with IV crystalloids (eg, 0.9% sodium chloride, lactated Ringer solution) is an important intervention aimed at preventing circulatory collapse resulting from fluid losses (eg, vomiting, diarrhea) and NPO status (Option 3).
(Option 1) Pain medications may be administered to promote comfort but should be administered via IV route to maintain NPO status in case of emergency surgery. In addition, circulation takes priority over pain medication.
(Options 2 and 4) Blood and urine testing often is prescribed to assist with treatment and care decisions. However, the nurse should prioritize circulatory status over obtaining laboratory specimens.
Educational objective:
Nurses caring for clients with appendicitis should
prioritize client care according to the ABCs (ie, Airway, Breathing, Circulation). Initiating
fluid resuscitation with IV crystalloids (eg, 0.9% sodium chloride) is a priority action that
prevents circulatory collapse resulting from fluid losses (eg, vomiting, diarrhea) and NPO status.
Lecture References :
- Adult Health - Appendicitis
Question
The nurse auscultates the heart sounds of a 77-year-old client with chronic heart failure. Which heart sound should the nurse document? Listen to the audio clip. (Headphones are required for best audio quality.)
| 1. Pericardial friction rub | |
| 2. S1, S2, no adventitious sounds | |
| 3. S3 extra heart sound | |
| 4. Systolic murmur |
Explanation
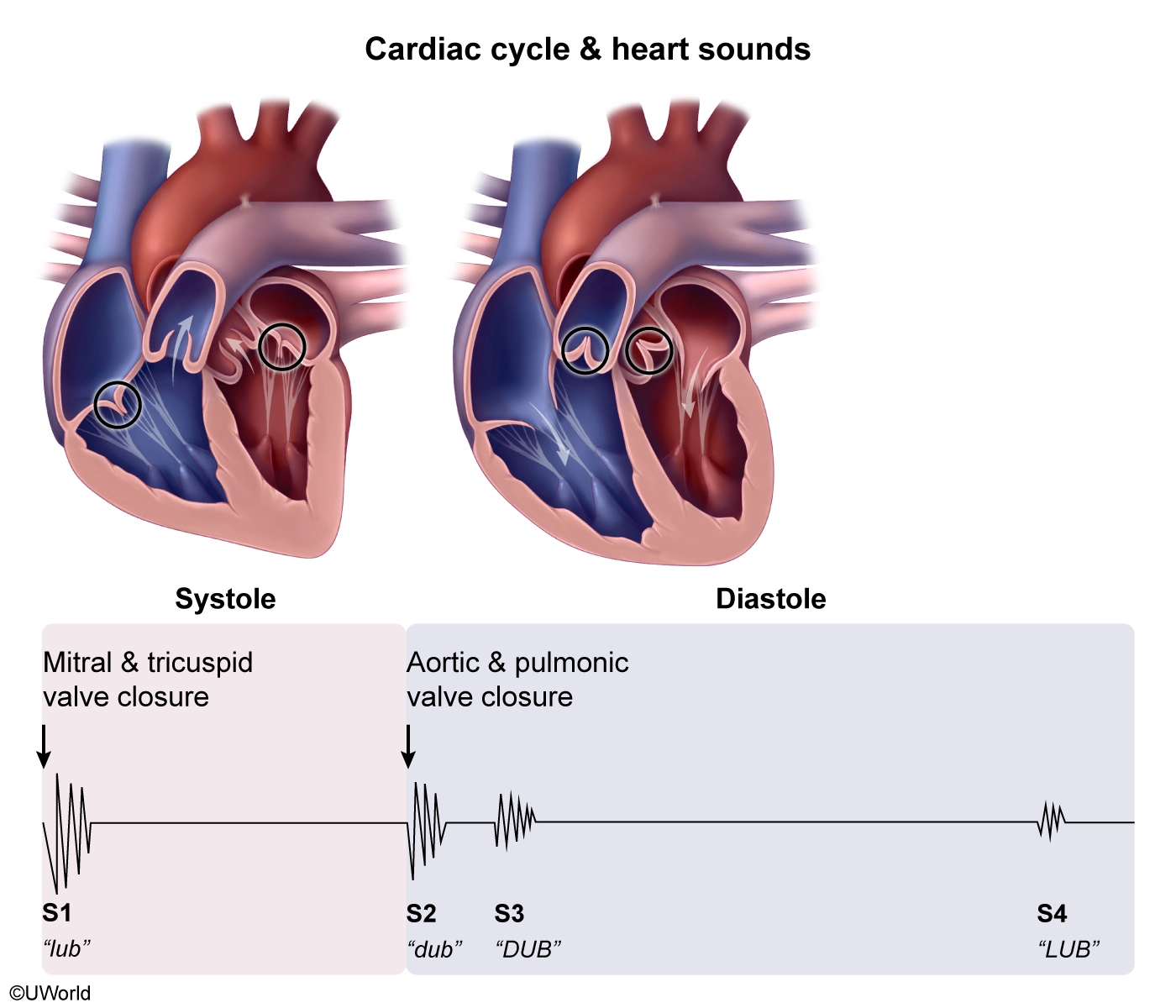
S1 and S2 are the normal "lub-dub" heart sounds that result from closure of valves. Systole occurs between S1 and S2, with S1 indicating closure of the atrioventricular (tricuspid, mitral) valves and S2 indicating closure of the pulmonic and aortic valves.
S3 is an adventitious (extra) heart sound heard as "DUB" immediately following S2 (Option 3). S3 occurs during early diastole as a result of rapid ventricular filling and is a normal finding in children and young adults. In older adults, S3 is an abnormal finding that often indicates heart failure because the sound results from decreased ventricular compliance.
S3 can be difficult to distinguish from S4. S4 is a "LUB" sound that occurs immediately before S1, during late diastole, and indicates ventricular hypertrophy.
(Option 1) A pericardial friction rub is a creaky, grating sound heard throughout systole and diastole. Friction rub occurs with pericarditis and is due to friction between inflamed layers of pericardium.
(Option 2) S1 and S2 are the normal heart sounds heard during cardiac auscultation.
(Option 4) A murmur is a swooshing, blowing, or rumbling sound caused by turbulent blood flow (eg, from valve regurgitation or stenosis).
Educational objective:
S3, the third heart sound, is a "DUB" sound that
immediately follows S2. It is a normal finding in children and young adults. S3, an
abnormal finding in older adults, often indicates heart failure.
Question
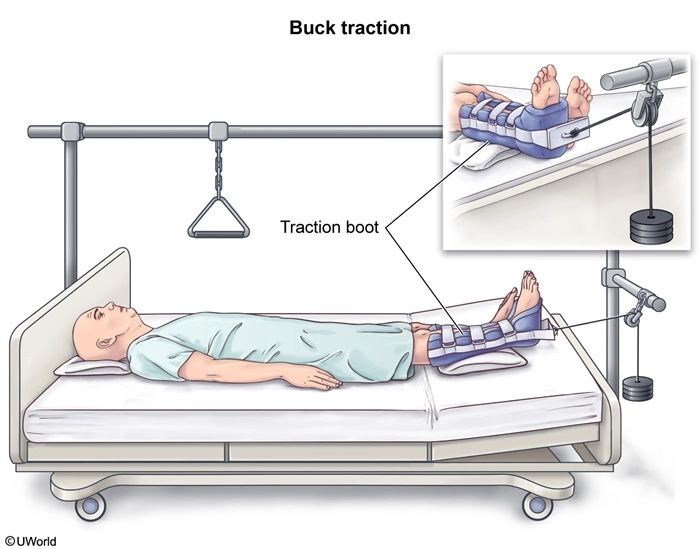
The nurse is caring for a client who has a hip fracture and is placed in Buck traction. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
| 1. Place the client on the affected side. | |
| 2. Monitor the client for skin breakdown. | |
| 3. Perform frequent neurovascular checks. | |
| 4. Keep the affected extremity in a neutral position. | |
| 5. Ensure that the client receives adequate pain relief. |
Explanation
Buck traction is a type of skin traction used to immobilize hip fractures and reduce pain and spasm until the client can undergo surgical repair of the fracture. A traction boot is applied to the leg, below the fracture site. A weight gently and continuously pulls on the leg and hip, helping maintain alignment of the extremity. The nurse should ensure that the traction boot is fitted properly and that the extremity remains straight in a neutral position (Option 4).
Skin traction exerts pressure on the nerves, blood vessels, and soft tissue. The nurse should frequently assess the skin integrity and neurovascular status (eg, pulse, capillary refill, color, temperature, sensation, movement) of the affected extremity (Options 2 and 3). Overall pain level and efficacy of administered pain medications should be monitored closely, as increasing pain may indicate neurovascular compromise (Option 5).
(Option 1) Placing a client in Buck traction on the affected side can cause more injury. Side-to-side position changes cause the affected extremity to be adducted or abducted, which, when paired with the force of traction, can increase spasm and pain and contribute to neurovascular and orthopedic compromise.
Educational objective:
Buck traction is used to
immobilize hip fractures and reduce pain and spasm until the fracture can be repaired
surgically. Nursing interventions include frequent assessment of skin integrity and
neurovascular status; maintaining the affected extremity in a straight, neutral position; and
ensuring adequate pain relief.
Lecture References :
- Adult Health - Traction
Question
The nurse is assigned to care for four clients. Which of the following clients should the nurse see first? Click the exhibit button for additional client information.
| 1. Female client who had an arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with sling immobilization and reports moderate swelling and tingling of the hand and fingers | |
| 2. Female client who had an open reduction and internal fixation of the tibia and reports severe pain and pressure under the cast and inability to move the toes | |
| 3. Male client who has two new prosthetic legs applied after traumatic, bilateral, below-the-knee amputation and reports crushing pain in the amputated areas | |
| 4. Male client who has a hematocrit of 37% (0.37) and hemoglobin of 12.5 g/dL (125 g/L) and is prescribed enoxaparin 1 day after a total hip arthroplasty |
Explanation
| Clinical manifestations of compartment syndrome (7 Ps) | |
|---|---|
|
Paresthesia (early sign) |
Tingling, numbness, burning |
| Pain | Out of proportion to injury, unrelieved by medication |
| Pressure | Taut skin, cast fits too tightly |
| Pallor | Pale skin tone, decreased color, white, gray |
|
Pulselessness (uncommon) |
Possibly weakened or lost |
| Poikilothermy | Cool skin temperature, matches room temperature |
|
Paralysis (late sign) |
Weakness, loss of motor activity |
Compartment syndrome occurs when swelling in a tissue compartment causes compression of arteries and nerves, typically after a direct injury (eg, fracture, dislocation) or medical device placement (eg, cast, splint). Tissue perfusion and nerve function distal to the swelling become impaired, causing signs of neurovascular compromise (eg, severe, unrelenting pain; paralysis) due to tissue ischemia. Without relieving compartment pressure (ie, cast removal, fasciotomy), ischemia leads to permanent nerve and tissue damage and/or loss of limb (Option 2).
(Option 1) Edema and numbness or tingling (paresthesia) of the hands and fingers commonly occur from inappropriate sling application. Numbness and tingling are also early signs of compartment syndrome. However, the client with late signs of compartment syndrome (eg, paralysis) should be seen first.
(Option 3) Clients with amputations may experience phantom limb pain that is severe and described as burning or crushing and requires pain management. However, limb-threatening emergencies should be managed first.
(Option 4) Slightly decreased hematocrit and hemoglobin levels are expected after hip arthroplasty due to intra- and postoperative blood loss.
Educational objective:
Compartment syndrome is a condition of impaired
circulation due to increased tissue pressure, often from edema or medical devices. Clients
with signs of compartment syndrome (eg, severe, unrelenting pain; paralysis) require immediate
assessment and intervention to prevent permanent tissue damage or loss of limb.
- Adult Health - Compartment Syndrome
Question
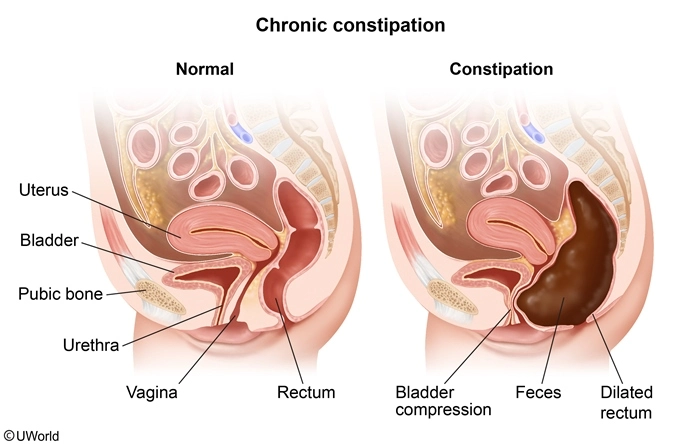
The nurse is reinforcing teaching about constipation prevention to a client. Which of the following client statements indicate appropriate understanding of the teaching? Select all that apply.
| 1. "Drinking more caffeinated drinks such as tea and soda helps to stimulate the bowel." | |
| 2. "Having a routine for bowel movements is important, but I should not wait if I feel the urge." | |
| 3. "I can use an over-the-counter laxative every other day if needed." | |
| 4. "I should try to eat more fruits and vegetables every day." | |
| 5. "Increasing my daily exercise level may help keep my bowel movements regular." |
Explanation
Constipation is a symptom of many disease processes (eg, Parkinson disease, diabetic neuropathy, depression), procedures (eg, abdominal surgery, bowel manipulation), and medications (eg, anticholinergics, diuretics, opioids). Immobility, low-fiber diets, decreased fluid intake, and irregular bowel habits increase the likelihood of constipation. Educate clients to prevent constipation by:
- Encouraging a healthy bowel regimen (eg, avoid delaying defecation if the urge is felt, defecate at the same time daily when possible, track bowel movements to identify changes in patterns) (Option 2)
- Increasing consumption of fruits and vegetables to reach a daily fiber intake of at least 20 g (unless contraindicated) because fiber softens and increases the bulk of stool, which promotes defecation (Option 4)
- Increasing daily exercise because activity stimulates peristalsis and promotes defecation (Option 5)
- Drinking 2-3 L of noncaffeinated fluids daily (unless contraindicated), which prevents drying and hardening of stool in the colon
(Option 1) Clients should avoid caffeinated beverages, which promote diuresis and dehydration and may lead to constipation.
(Option 3) Clients should avoid using laxatives and enemas unless prescribed by a health care provider because overuse can result in physical and psychological dependency.
Educational objective:
Constipation is a symptom of many disease processes, procedures, and medications. To prevent
constipation, educate the client to increase daily fiber intake, drink 2-3 L of fluids daily,
increase daily activity levels, and initiate a bowel regimen (eg, avoiding delay of defecation,
defecating at the same time each day).
Lecture References :
- Adult Health - Constipation
Question
The nurse is assigning client care tasks to unlicensed assistive personnel. Which statement by the nurse is appropriate?
| 1. "I need you to take vital signs on all clients in rooms 1 through 10 this morning." | |
| 2. "Mrs. Jones fell out of bed during the night while walking to the commode. Please monitor her closely." | |
| 3. "Please ensure that Mr. Garcia in room 8 ambulates several times." | |
| 4. "Please take Mr. Wu's vital signs in 10 minutes and let me know if his systolic blood pressure is <100." |
Explanation
| Five rights of delegation | |
|---|---|
| Right task |
|
| Right circumstances |
|
| Right person |
|
|
Right direction/ communication |
|
|
Right supervision/ evaluation |
|
When assigning client care, the nurse must consider the five rights of delegation. Right direction/communication involves clear and precise instructions about assigned tasks, including any specific information necessary for completion. Necessary information includes the specific tasks (eg, take vital signs), the time frame (eg, in 10 minutes), and when to report back to the nurse (eg, if systolic blood pressure is <100) (Option 4).
(Option 1) Assigning unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) to measure vital signs "this morning" does not provide a clear time frame (eg, in 1 hour) for completion. In addition, there is no communication about what the nurse expects in terms of follow-up.
(Option 2) Instructing the UAP to monitor the client closely is an unclear direction because it does not provide specific actions to perform (eg, "Set the bed alarm."), time intervals for performance (eg, "Check on the patient every hour."), or criteria to report to the nurse (eg, "Notify me if the client attempts to exit the bed unassisted.").
(Option 3) Instructing the UAP to assist with ambulation "several times" does not give a specific time frame or distance for the client to ambulate. The nurse should also communicate the conditions or aids needed to accomplish the task (eg, walks with assistance or rolling walker).
Educational objective:
Nurses assigning client care to unlicensed assistive personnel must consider the five rights of delegation. Right direction/communication involves providing clear instructions about the assigned tasks, specific information needed for task completion, the time frame, and when to report back to the nurse.
Make Exam Day Feel Like Déjà Vu
“I swear I saw a UWorld question on the NCLEX!” We hear it constantly, and that’s by design. You won’t see our exact questions on the exam, but with 40+ nurse authors crafting high-fidelity scenarios to strict NCSBN standards, you’ll feel like you did.
Build Total Confidence with Total Coverage
Master every item type, subject, and system on the NCLEX-RN or PN. Target specific topics with custom practice tests and walk into the test center with total confidence.
Everything You Need to Pass
Go beyond NCLEX practice questions with computer adaptive test (CAT) practice tests, diagnostic reports, engaging video lectures, a digital notebook, spaced-repetition flashcards, readiness assessments, and more.
Every Item Type
Prepare for the NCLEX with every official item format. Every item type is covered, including Case Studies, Bow-tie, and Matrix, plus standard Select All that Apply (SATA), so there are no surprises on test day.
Every Subject
Get full coverage of the NCSBN test plan and all Client Needs categories. Master essential nursing topics from Pharmacology and Pediatrics to Mental Health and Maternity.
Every System
Achieve head-to-toe competence. Our Question Bank (QBank) covers all physiological systems, including Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Neurological, Gastrointestinal, Renal, and Endocrine health.
Everywhere
Create unlimited practice tests, review high-yield video lectures, flashcards, and notes. Your NCLEX prep progress syncs across all your devices for an always up-to-date and seamless experience.
Everything You Need to Pass
Go beyond NCLEX practice questions with computer adaptive test (CAT) practice tests, diagnostic reports, engaging video lectures, a digital notebook, spaced-repetition flashcards, readiness assessments, and more.
Every Item Type
Prepare for the NCLEX with every official item format. Every item type is covered, including Case Studies, Bow-tie, and Matrix, plus standard Select All that Apply (SATA), so there are no surprises on test day.
Every Subject
Get full coverage of the NCSBN test plan and all Client Needs categories. Master essential nursing topics from Pharmacology and Pediatrics to Mental Health and Maternity.
Every System
Achieve head-to-toe competence. Our Question Bank (QBank) covers all physiological systems, including Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Neurological, Gastrointestinal, Renal, and Endocrine health.
Everywhere
Create unlimited practice tests, review high-yield video lectures, flashcards, and notes. Your NCLEX prep progress syncs across all your devices for an always up-to-date and seamless experience.
We Measure Our Success by Your Success

I love this product. I am using it in preparation for NCLEX, but I wish I had used it while I was studying in nursing school. The rationales are concise and to the point, and the illustrations help with understanding the material. Great product. Highly recommend it.”

UWorld definitely prepares you for the NCLEX! The best test bank. So informative and helpful! It is definitely worth getting. The rationales are amazing and go in depth for each topic. I have tried other question banks for the NCLEX and found UWorld to be the best.”

The rationales are exceptional. They really help me understand the whole picture and then some. Reading through why the answer I chose was incorrect also helps me understand in which circumstance that answer choice would be correct.”
Every NextGen NCLEX Question Type, Covered
Pass with confidence by practicing the exact question formats you’ll face on exam day. From Bow-ties to Trend questions, if it’s on the NCLEX, it’s in our QBank.
Extended Multiple Response Questions
Select 1 or more correct answers. This includes Select All That Apply (SATA), multiple response grouping items, and select-N formats. These question types require careful evaluation of all possible answers.
Drag and Drop Questions
Drag and drop 1 or more answer choices into designated boxes within a sentence (cloze) or into a multiple-response answer key box (extended drag and drop).
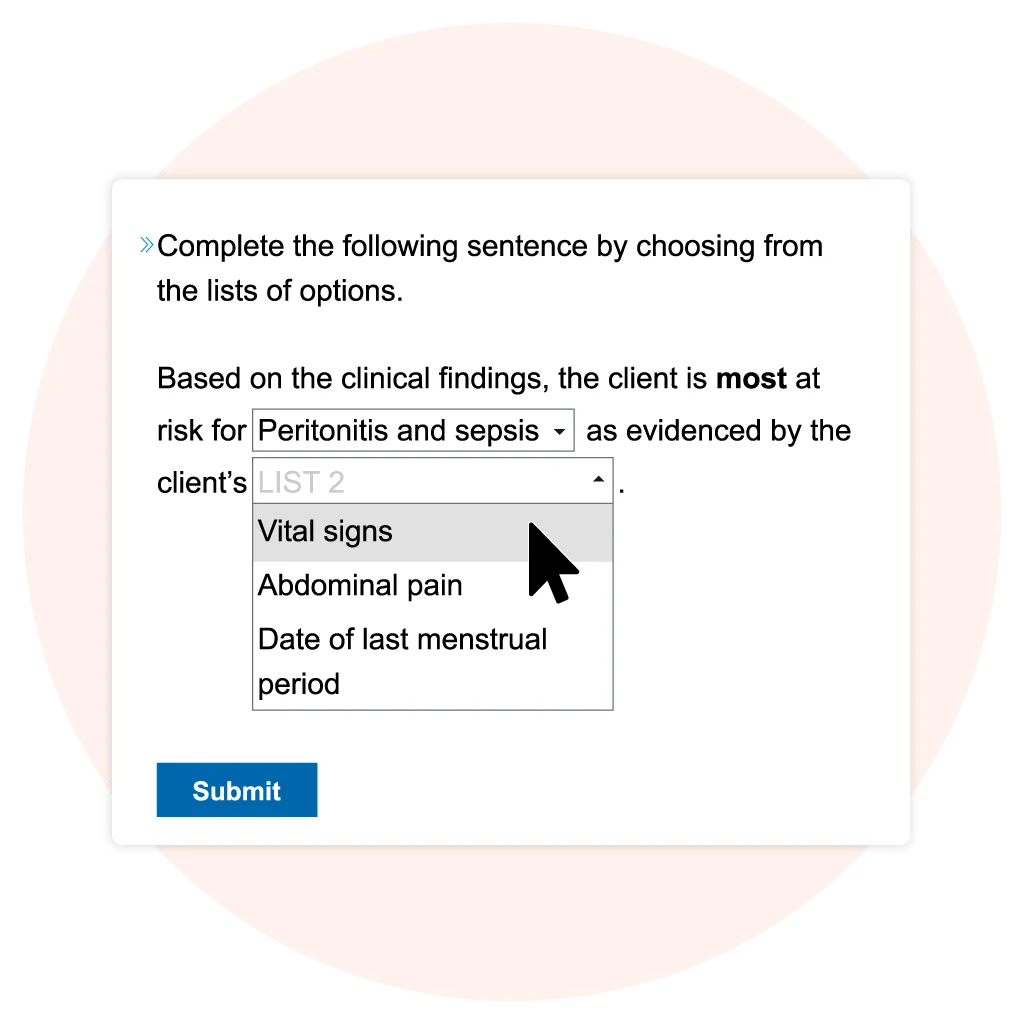
Drop-Down Questions
Complete a sentence, passage, or table by selecting the correct response from a drop-down list. Drop-down answer choices may appear in a cloze format (sentence, passage, rationale statement) or within a table.
Highlight Questions
Identify key information by highlighting words or phrases within a sentence, passage, or table. These questions test the ability to recognize critical details needed for clinical decision-making.
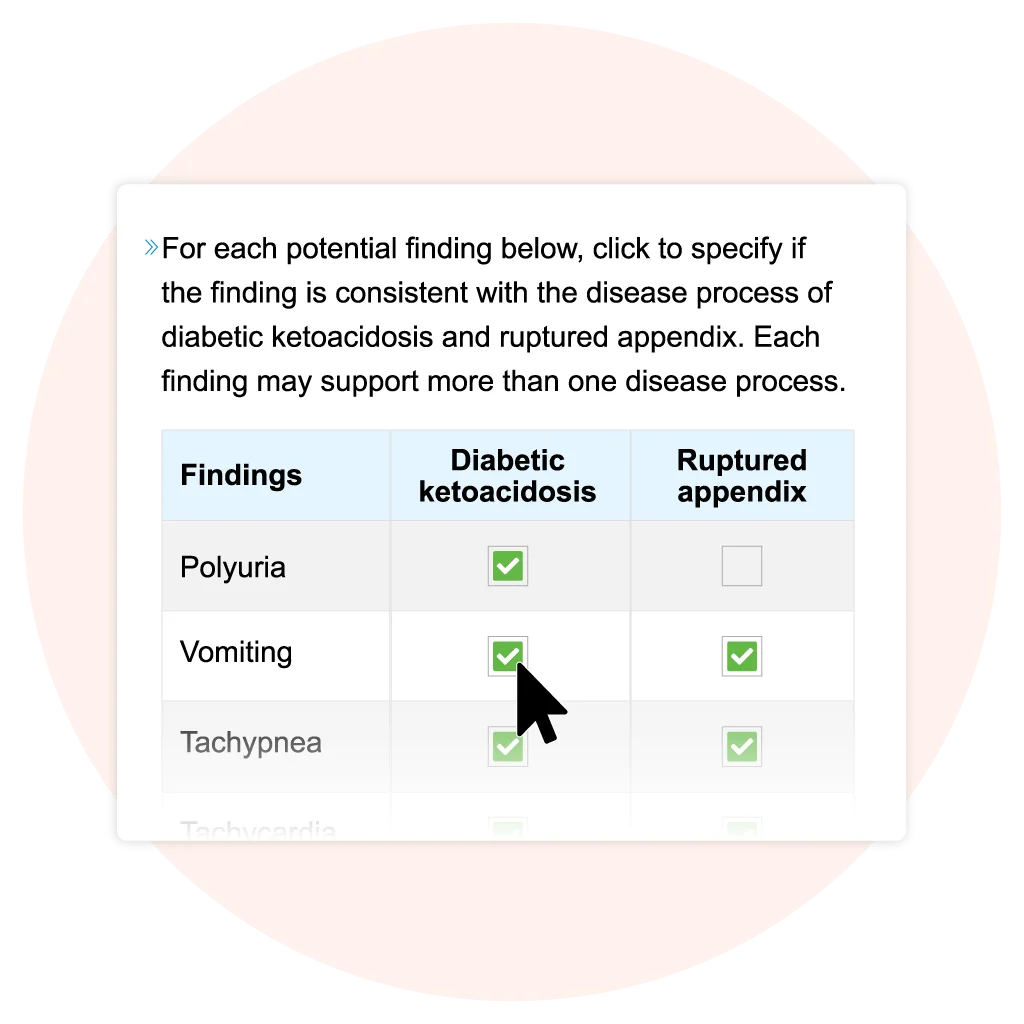
Matrix/Grid Questions
Select 1 or more options for each row or column that apply to the clinical information provided. Square buttons indicate that more than 1 answer can be selected, while radio buttons indicate that only 1 answer can be selected.
Bow-tie Questions
Assess all 6 steps of the Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (CJMM) in a single item. Candidates must read a scenario and then drag and drop 5 answer choices into the correct location in the answer key.
Trend Questions
Analyze patterns over time using data such as vitals, labs, or patient progress. These questions require recognizing trends to determine appropriate clinical actions.
Extended Multiple Response Questions
Select 1 or more correct answers. This includes Select All That Apply (SATA), multiple response grouping items, and select-N formats. These question types require careful evaluation of all possible answers.
Drag and Drop Questions
Drag and drop 1 or more answer choices into designated boxes within a sentence (cloze) or into a multiple-response answer key box (extended drag and drop).
Drop-Down Questions
Complete a sentence, passage, or table by selecting the correct response from a drop-down list. Drop-down answer choices may appear in a cloze format (sentence, passage, rationale statement) or within a table.
Highlight Questions
Identify key information by highlighting words or phrases within a sentence, passage, or table. These questions test the ability to recognize critical details needed for clinical decision-making.
Matrix/Grid Questions
Select 1 or more options for each row or column that apply to the clinical information provided. Square buttons indicate that more than 1 answer can be selected, while radio buttons indicate that only 1 answer can be selected.
Bow-tie Questions
Assess all 6 steps of the Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (CJMM) in a single item. Candidates must read a scenario and then drag and drop 5 answer choices into the correct location in the answer key.
Trend Questions
Analyze patterns over time using data such as vitals, labs, or patient progress. These questions require recognizing trends to determine appropriate clinical actions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What makes UWorld’s NCLEX practice questions unique?
UWorld is the industry leader and the National Student Nurses’ Association (NSNA) preferred choice for NCLEX prep because our NCLEX practice questions are crafted through a rigorous creation process. A dedicated team of over 40 practicing nurses and nurse educators writes, updates, and reviews every item to ensure they meet strict NCSBN standards and match the difficulty of the actual exam.
- Expert Visuals: Our clinical team works alongside professional designers with master’s degrees to create a visual language proven to boost retention. We use high-quality medical illustrations to help you visualize difficult concepts, making complex NCLEX-RN practice questions easier to understand.
- Clinical Judgment: We don’t just ask you to memorize facts; we teach you how to think like a nurse and build clinical judgment with in-depth explanations for every answer choice.
- Realistic Interface: Our platform mimics the actual NCLEX test questions interface, reducing test-day anxiety by ensuring you are familiar with the screen layout and tools.
- Active Learning: By using our practice NCLEX questions, you engage in active recall, a scientifically proven strategy that improves long-term retention compared to passive reading.
How many NCLEX practice questions does UWorld’s NCLEX QBank offer?
Between NCLEX-RN and PN, UWorld offers 5,000+ NCLEX practice questions. Our comprehensive QBanks ensure you have everything you need to pass the NCLEX the first time:
- NCLEX-RN: Our QBank features 3,200+ NCLEX-RN questions, covering all major client needs categories and body systems.
- NCLEX-PN: We provide 2,050+ NCLEX-PN practice questions specifically tailored to the practical/vocational nursing scope of practice.
- Assessment Tests: In addition to the QBank, we offer self-assessment tests comprising unique NCLEX exam questions not found in the regular study bank.
How many questions are on the NCLEX?
The NCLEX uses Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT), so the exam length varies for each candidate.
- Question Count: For both the NCLEX-RN and NCLEX-PN, candidates will answer a minimum of 85 questions and a maximum of 150 questions.
- Timing: The maximum time allowed for the exam is 5 hours. Every exam includes Next Gen NCLEX items designed to measure clinical judgment. Our CAT practice tests mirror this variable length and structure to simulate the real testing environment.
What nursing subjects and systems are covered in UWorld's NCLEX practice questions?
Our NCLEX practice questions are comprehensively organized to cover every major subject area and body system outlined in the NCSBN test plan. This allows you to create a personalized study plan by filtering NCLEX exam questions based on your specific needs.
- Subjects: We provide extensive coverage of Adult Health (Medical-Surgical), Maternal-Newborn, Pediatric Nursing, Psychiatric-Mental Health, Fundamentals, Leadership & Management, and Pharmacology.
- Systems: You can focus your practice NCLEX questions on specific body systems, including Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Neurological, Gastrointestinal, Musculoskeletal, Endocrine, Reproductive, and Immune/Oncology.
Whether you are reviewing NCLEX-RN or NCLEX-PN practice questions, using these subject-specific filters helps you target weak areas and master the content effectively.
Are there separate practice questions available for the NCLEX-RN and NCLEX-PN?
Yes, we offer distinct resources for each exam because the scope of practice differs between registered nurses and licensed practical/vocational nurses.
- NCLEX-RN: You can access specific NCLEX-RN practice questions that focus on the management of care and complex clinical judgment expected of RNs.
- NCLEX-PN: We provide dedicated NCLEX-PN practice questions that align with the PN test plan, focusing on coordination of care and practical nursing tasks. Ensure you select the correct NCLEX practice quiz for your licensure path to get the most accurate assessment.
Do the practice questions provide detailed rationales for correct and incorrect answers?
Absolutely. The hallmark of UWorld is our industry-leading rationales. Whether you are using our paid QBank or our free NCLEX practice questions, every single question comes with a detailed explanation.
- Visual Learning: We use vivid illustrations, charts, and diagrams to explain complex concepts.
- Comprehensive Answer Explanations: We explain why the correct answer is right and, just as importantly, why the distractors are incorrect. This approach transforms every NCLEX practice question into a high-yield learning opportunity, helping you master the “why” behind nursing interventions.
Do UWorld’s NCLEX practice questions include every item type?
Yes. Our NCLEX-RN practice questions and NCLEX-PN practice questions are comprehensive and include every item type you will encounter on the official NCLEX exam. To ensure you are fully prepared for the NCLEX, our QBank covers:
- Next Gen Item Types: We include all question formats, including Extended Multiple Response, Extended Drag-and-Drop, Cloze (Drop-Down), Enhanced Hot Spot (Highlighting), Matrix/Grid, Bow-tie, and Trend questions.
- Case Studies: You will practice with unfolding clinical scenarios that mirror the real exam’s structure to test your clinical judgment.
- Traditional Item Types: We continue to feature high-yield Multiple Choice, Select All That Apply (SATA), Ordered Response, and Audio/Graphic NCLEX questions.
Practicing with these varied NCLEX test questions helps build the muscle memory and confidence required for success on test day.
What specific clinical judgment skills are NCLEX practice questions designed to measure?
The NCLEX focuses on the NCSBN Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM). Our NCLEX-RN questions and NCLEX-PN questions are built to test the 6 cognitive skills of this model:
- Recognize Cues: Identifying relevant data.
- Analyze Cues: Connecting data to clinical presentation.
- Prioritize Hypotheses: Ranking potential issues.
- Generate Solutions: Planning interventions.
- Take Action: Implementing the plan.
- Evaluate Outcomes: Assessing the patient’s response. Practicing with NCLEX model questions that target these specific skills is essential for passing the NCLEX.
Does UWorld include dosage calculation questions?
Can I sign up for a full free trial to access more than just the sample questions?
What is the “active learning” approach with practice questions?
Active learning is the core of UWorld’s methodology. Instead of passively reading a textbook, you engage with NCLEX practice questions by solving problems and receiving immediate feedback.
- Application: You apply knowledge to clinical scenarios rather than memorizing facts through our comprehensive NCLEX practice questions.
- Immediate Remediation: You review detailed rationales immediately after answering each practice question.
- Retention: This process of testing and reviewing builds stronger neural connections, leading to better retention and recall during the actual NCLEX exam.
Our NCLEX practice questions are designed to keep you actively engaged, which is proven to be more effective than passive review.
Does UWorld fully prepare me for the Next Generation NCLEX (NGN)?
Yes. UWorld is fully aligned with the Next Generation NCLEX and the NCSBN Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM).
We have updated our entire QBank to ensure you are ready for the new exam format. Here is how we prepare you:
- All Item Types: Practice with thousands of NCLEX questions, including hundreds of NGN questions.
- Real-World Scoring: Our platform uses the exact same partial-credit scoring rules as the actual NGN, giving you a realistic picture of your performance.
- Simulated Interface: Our interface mimics the actual NCLEX screen down to the pixel. By the time you sit for the exam, the navigation and layout will feel like second nature.
- Clinical Judgment Focus: Our questions don’t just test facts; they challenge you to recognize cues, analyze data, and prioritize care, exactly what the CJMM requires of new nurses.
Can I use specific NCLEX practice questions to focus on my weak areas?
Yes. UWorld allows you to create unlimited custom NCLEX practice tests.
You can filter questions by:
- Subject (e.g., Adult Health, Pharmacology, Pediatrics, Mental Health)
- Body system (e.g., Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Neurological, GI)
- Question status (Unused, Incorrect, Marked)
- Difficulty level
After each test, detailed performance analytics help you identify gaps and focus your study time where it matters most.